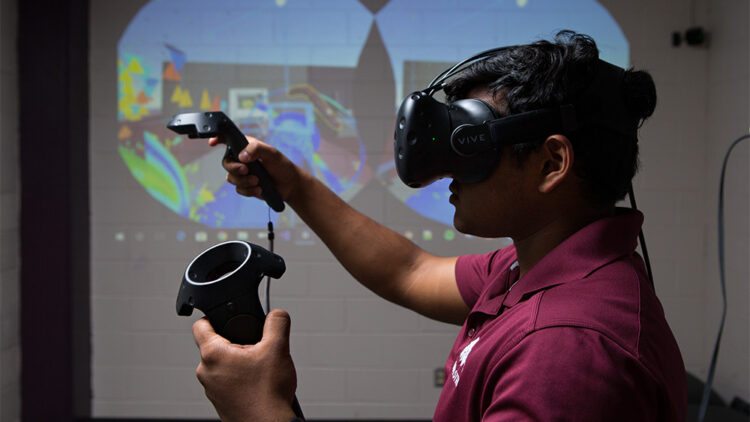
The Evolution of Training: Why VR is the Next Frontier
For decades, learning has been a passive activity. Trainees sat in classrooms, read documents, or clicked through generic online courses. While these methods offered knowledge transfer, they critically lacked the sense of presence and practical application necessary for true skill mastery and high-stakes scenario preparedness.
Virtual Reality changes this dynamic entirely. By leveraging sophisticated hardware primarily Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) and realistic, computer-generated environments, VR immerses the user completely. This immersion is not a mere distraction; it is the core mechanism that boosts knowledge retention and confidence by turning theoretical knowledge into muscle memory.
Defining Virtual Reality in the Context of Training
Before diving into applications, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental technology driving this revolution.
- Immersion and Presence: VR is fundamentally defined by its ability to create a sense of being physically present in a non-physical world. In training, this means an employee can genuinely feel they are on a factory floor, operating complex machinery, or interacting with a virtual customer. This state, known as “Presence,” is what makes the training so effective.
- Haptic Feedback: Often utilized via specialized gloves or controllers, haptics introduce the sense of touch, allowing trainees to “feel” virtual objects, further increasing the realism of the simulation.
- 6 Degrees of Freedom (6DOF): Unlike simpler 3DOF systems, 6DOF allows the user to move forward/backward, up/down, and left/right, in addition to rotational movements (pitch, yaw, roll). This positional tracking is vital for realistic, hands-on training where movement and spatial awareness are key skills.
Key Benefits of Implementing VR Training Solutions
The adoption of VR in training is accelerating across various industries, from healthcare and retail to manufacturing and energy. This widespread integration is driven by several measurable, compelling advantages over conventional methods.
A. Mitigating Risk in High-Stakes Scenarios
In fields like oil and gas, surgery, or heavy equipment operation, a single mistake during real-world training can lead to catastrophic consequences injury, loss of life, or damage to multi-million dollar assets. VR offers a perfectly safe, consequence-free sandbox.
Trainees can practice emergency shutdowns, complex surgical procedures, or hazardous material handling repeatedly until they achieve proficiency. They are encouraged to make mistakes, learn from them immediately, and reinforce the correct actions without any real-world repercussions. This risk-free environment is perhaps the most significant benefit for industrial and medical training.
B. Dramatic Improvement in Knowledge Retention
Numerous studies consistently show that experiential learning—learning by doing—leads to substantially higher rates of knowledge recall than purely passive methods. The multi-sensory and emotional input inherent in an immersive VR experience strengthens memory pathways.
- VR learners exhibit significantly higher emotional connection to the content compared to classroom or e-learning participants, translating to a deeper, more lasting understanding.
- The interactive nature, coupled with the ability to repeat complex simulations, moves information from short-term to long-term memory much more effectively.
C. Reducing Training Time and Costs
While the initial investment in hardware and custom content development can be a factor, VR training slashes long-term operational costs and time-to-competency.
- Accelerated Learning: VR programs can often reduce the time required to complete training by as much as 40-75% compared to traditional classroom settings. What took a full day can sometimes be mastered in a few concentrated hours of VR practice.
- Eliminating Travel and Logistics: Training a global workforce often involves significant travel costs, accommodation, and venue rental. VR training can be deployed anywhere, allowing employees to access high-quality, standardized training from their local office or even their home, saving millions in travel and logistics.
- Scalability and Consistency: Once a VR module is developed, it can be deployed to thousands of employees simultaneously with perfect consistency. Every single trainee receives the exact same, high-quality, up-to-date instruction, ensuring a uniform standard of expertise across the entire organization.
D. Boosting Employee Engagement and Focus
Modern employees, especially digital natives, often find traditional training formats monotonous and disengaging. VR, being a novel and highly interactive medium, naturally captures attention.
The HMD effectively blocks out external distractions, forcing a four-times higher focus rate during training sessions. Furthermore, the integration of gamification—using scores, badges, and progress tracking transforms compliance and skill-building into an enjoyable, competitive activity, significantly increasing motivation and completion rates.
Diverse Applications of Virtual Reality Training Across Industries
The versatility of VR allows it to be applied to a vast spectrum of learning objectives, far beyond simple technical skills.
1. Technical and Procedural Training (Hard Skills)
This is the most common use case, focusing on detailed, step-by-step physical skills.
- Manufacturing and Assembly: Training new operators on complex, multi-million-dollar machinery without risking equipment damage or using up valuable production time.
- Maintenance and Repair: Guiding technicians through intricate repair procedures, such as swapping out parts in an engine or fixing specialized lab equipment.
- Emergency Response: Simulating fire safety, chemical spills, or high-pressure control room scenarios, training personnel to remain calm and follow protocol under extreme duress.
2. Soft Skills and Interpersonal Training
VR’s power lies in its ability to simulate human interaction, making it perfect for developing nuanced soft skills.
- Customer Service and De-escalation: Role-playing difficult customer interactions with AI-driven virtual avatars, allowing employees to practice empathy and conflict resolution in a safe, judgment-free space.
- Diversity and Inclusion (D&I) Training: Allowing a user to “step into the shoes” of another, experiencing virtual scenarios from a different perspective to build genuine empathy and awareness of unconscious bias.
- Public Speaking and Presentation Skills: Practicing speeches in front of a simulated, realistic audience that provides instant feedback on eye contact, pace, and filler words.
3. Medical and Healthcare Training
The medical field has adopted VR to master skills where precision and quick decision-making are life-saving.
- Surgical Rehearsal: Surgeons can practice rare or complex procedures repeatedly on virtual patients, refining motor skills and procedure sequencing before operating on a real person.
- Anatomy and Diagnostics: Medical students can explore the human body in an interactive 3D environment that far surpasses static textbook diagrams.
- Clinical Communication: Training nurses and doctors on delivering sensitive news or handling emotionally charged patient/family conversations.
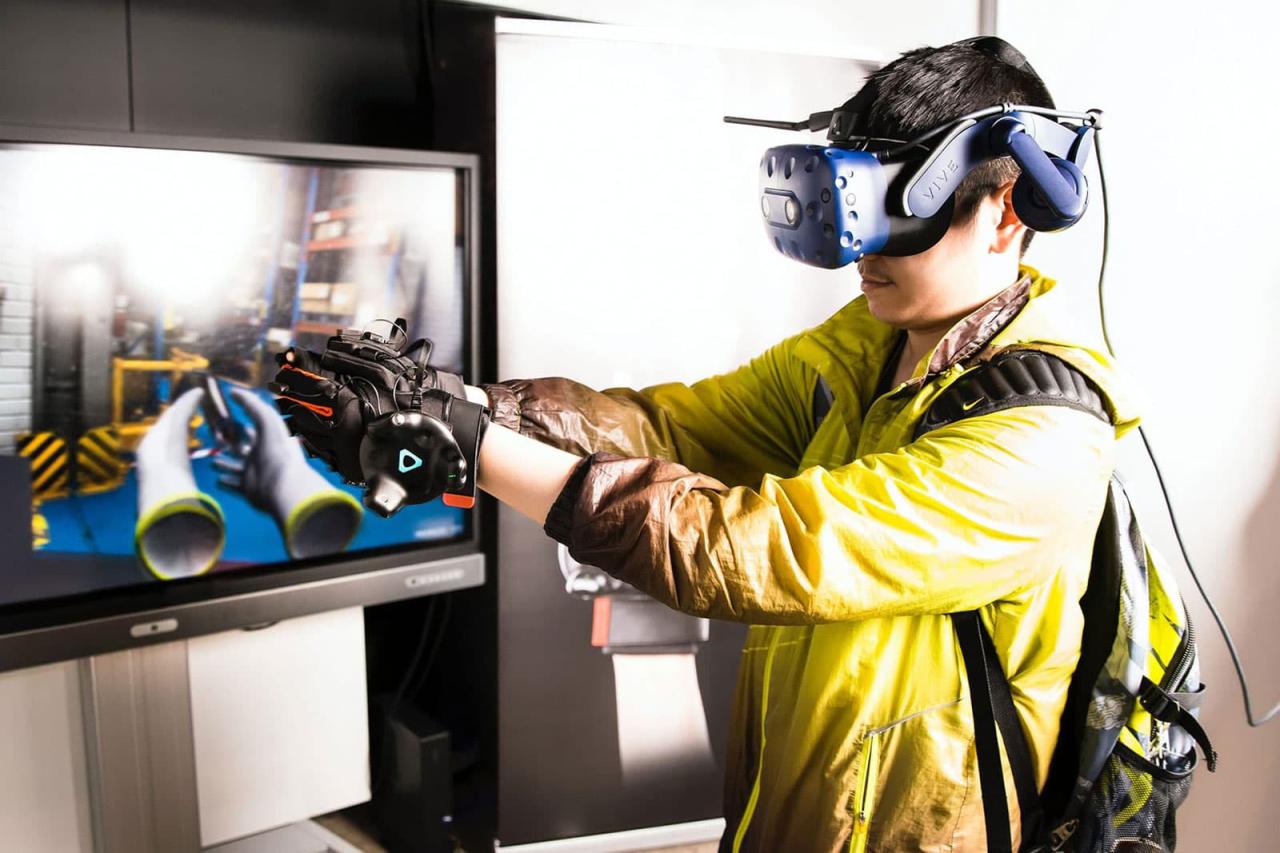

The Technology Stack: Components of an Effective VR Training System
Building a high-impact VR training program requires the integration of several key technological components.
A. Hardware: The Gateway to the Virtual World
- Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): The core piece of equipment. Modern standalone HMDs (like Meta Quest or Pico) are popular in corporate training due to their ease of deployment, lack of external wires, and relatively low cost compared to PC-tethered systems.
- Haptic Accessories: Gloves, vests, or specialized controllers that transmit tactile feedback to the user, enhancing the sensation of touching, grasping, or feeling impact in the simulation.
- Motion Tracking Systems: Cameras and sensors (internal or external) that accurately track the user’s position and movements in the physical world and translate them into the virtual environment.
B. Software: The Brains of the Operation
- Content Creation Platforms: Specialized development tools (often built on game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine) used to design and build the highly detailed, interactive 3D training environments and scenarios.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) Integration: The VR training must seamlessly report performance data back to the company’s existing LMS to track progress, compliance, and competency.
- Analytics and Assessment Tools: The most powerful feature of VR. The software tracks every micro-action: where the user looked (eye tracking), how quickly they reacted (latency measurement), and every procedural step they took. This provides granular, objective performance data far superior to a pass/fail quiz.
Designing for Success: Best Practices in VR Content Creation
To maximize ROI and training efficacy, content must be meticulously designed with both the learner and the learning outcome in mind.
A. Prioritize Realism and Fidelity
The environment must be visually and physically accurate enough to create a genuine sense of presence. For technical training, this means the virtual equipment must function exactly like its real-world counterpart. Low-fidelity or poorly rendered environments can break immersion and diminish the learning transfer.
B. Embrace Error-Based Learning
Design the scenarios to allow and encourage trainees to make mistakes. A powerful VR experience includes immediate, detailed feedback on the consequences of their actions.
The ability to instantly “rewind” and correct a catastrophic error is a learning luxury impossible in the real world.
C. Integrate Detailed Data Capture
The goal is not just to see if the user completed the task, but how they completed it. Track and record data on:
- Action Time: How long did it take the user to complete a task versus a highly skilled expert?
- Correct Procedure Adherence: Did they follow the mandated safety checklist sequence perfectly?
- Attention Metrics: Did the user look at the critical gauges or warning signs during a crisis?
This deep data allows trainers to pinpoint specific weaknesses and customize future training pathways.
Challenges and Future Outlook for VR Training Adoption
While the benefits are clear, VR adoption is not without its hurdles. Understanding and addressing these challenges is key to successful implementation.
A. Initial Cost and Content Development
The primary barrier is the upfront cost of hardware procurement and the significant expense involved in creating custom, high-fidelity content. Developing a detailed simulation requires specialized 3D modeling, programming, and subject matter expertise. Solutions are emerging, however, with more affordable, off-the-shelf VR training platforms designed for common corporate needs (e.g., leadership or soft skills).
B. Technical Support and Integration
Deploying and managing hundreds or thousands of HMDs requires new IT infrastructure and support. Ensuring seamless software updates, data integration with existing LMSs, and minimizing technical friction for the end-user remains a logistical challenge for large organizations.
C. Simulator Sickness
While modern HMDs have drastically reduced the issue of simulator sickness (nausea or disorientation), it can still occur due to factors like high latency (lag between head movement and display update) or poorly designed locomotion methods. Choosing high-quality hardware and following best practices in content design are critical to minimizing this risk.
The Future is Hybrid and Spatial
The future of VR training points toward a synergy of technologies:
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: AR overlays digital information onto the real world (e.g., smart glasses guiding a technician through a repair on a physical machine). The best learning programs will utilize both VR for pure simulation and AR for on-the-job guidance.
- AI-Driven Scenarios: Integrating advanced AI allows virtual avatars and environments to react dynamically, creating truly unique and challenging training scenarios that adapt to the learner’s performance, moving beyond scripted pathways.
- Persistent Virtual Workspaces: Beyond training, VR will serve as a virtual workspace, allowing global teams to collaborate in shared, persistent 3D spaces, further blurring the lines between work and learning.
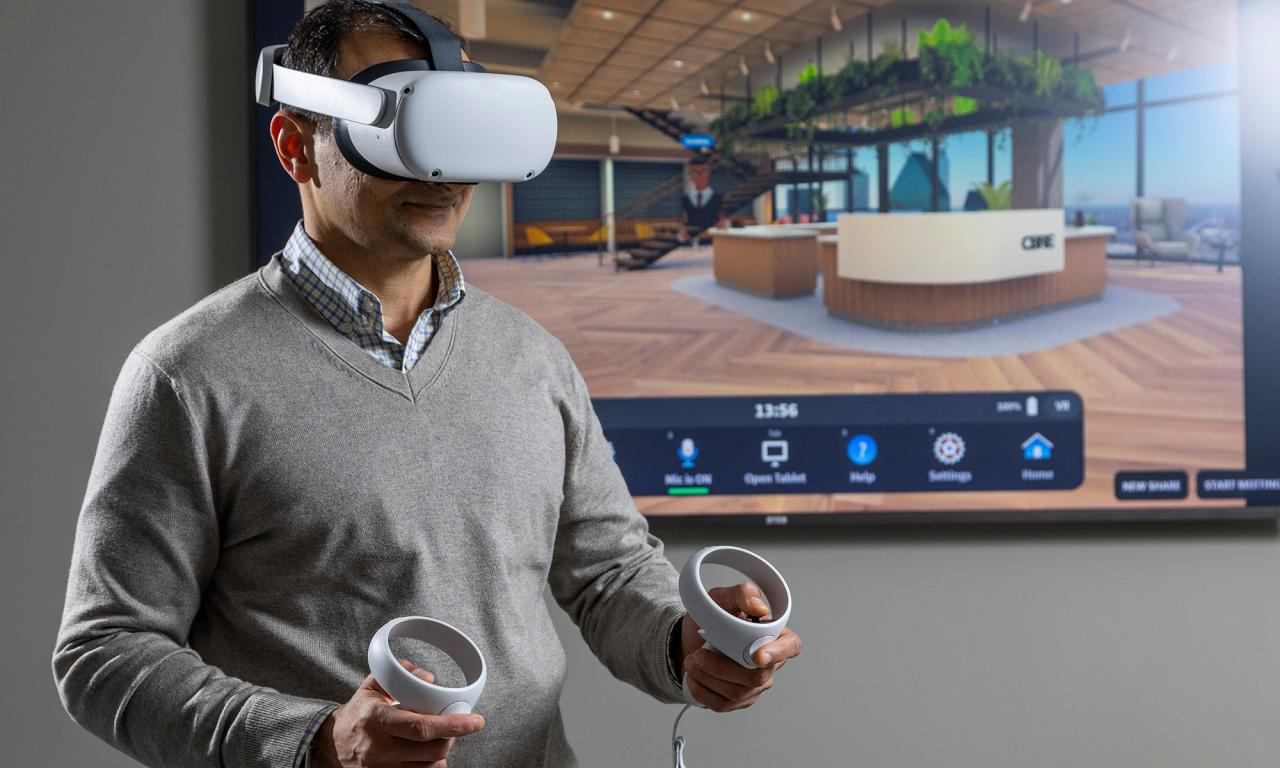

Conclusion: VR Training as a Strategic Imperative
The evidence is overwhelming: Virtual Reality training tools are fundamentally changing the return on investment in human capital. They offer unparalleled levels of engagement, retention, and safety that traditional methods simply cannot match. For any forward-thinking organization prioritizing operational efficiency, workforce competency, and a reduced risk profile, the question is no longer if to adopt VR, but how fast. By committing to high-quality content development, strategic deployment, and deep data analysis, companies can transform their training departments from cost centers into powerful engines for skill mastery and competitive advantage. The era of immersive, spatial learning is here, and those who embrace it today will lead the industries of tomorrow.